Iranian Knowledge-Based Firm Uses Headspace Method to Analyze Alcohol in Blood
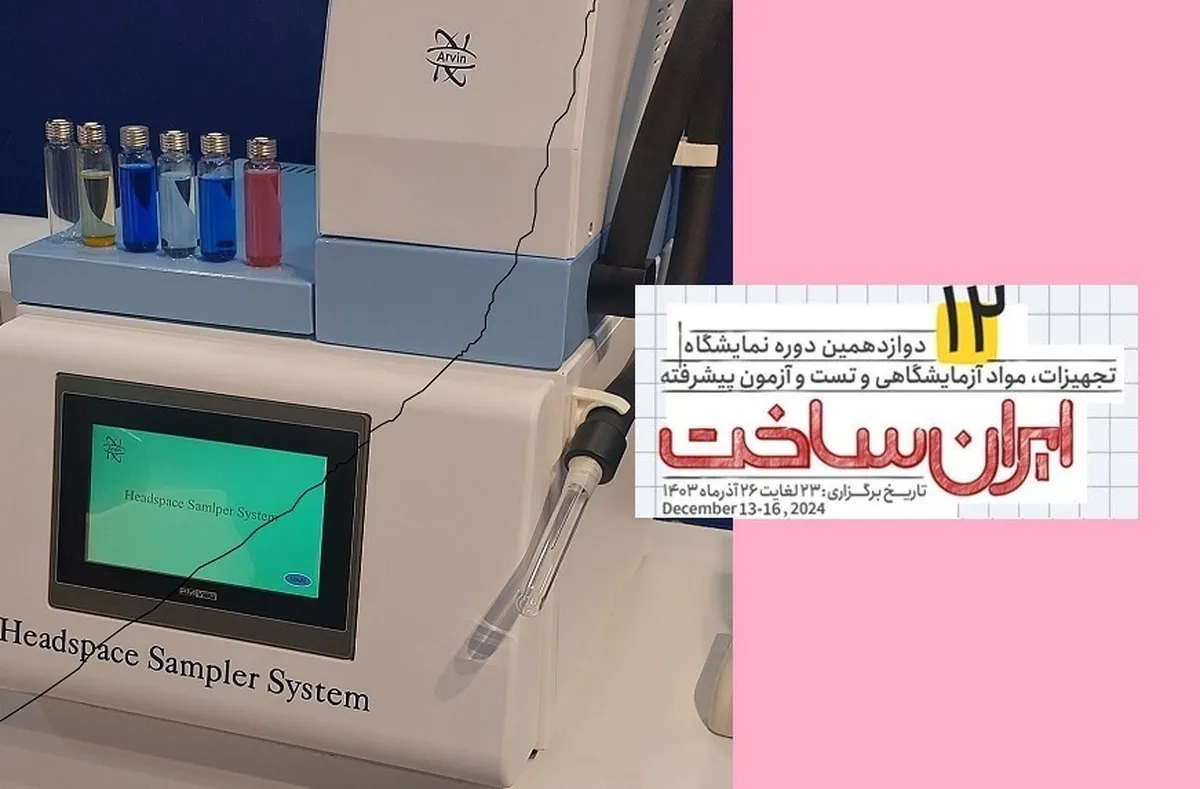
“Headspace is a method in which a sample is placed in a small sealed glass vial, and the gas phase part, called the headspace, is introduced into a gas chromatography separation column for detection and quantification,” said Moussavi, the chairman of the board of directors of the company.
“This allows the analyst to eliminate the sample pre-treatment step and focus on interpreting quantitative results and developing new analytical methods, providing more time for R&D assessment; actually, headspace is a convenient and fast sample pretreatment method in gas chromatography that eliminates complex and error-prone steps compared to other GC sample processing techniques and allows laboratory experts to obtain a large amount of useful information in a relatively short period of time,” he added.
The headspace sampling system is an automated equipment with an efficient and standard technique for testing volatile samples using a gas chromatography device. In this method, the sample to be analyzed is placed in glass containers (Vials) and, after being closed by special doors (Cap Crimp), it is placed in a heating chamber with the ability to adjust and control the temperature (Oven). After the appropriate equilibration time with each type of analyte has elapsed, volatile substances are created on the upper surface of the vial,” Moussavi said.
“Subsequently, the required part of the vapors created is directed to the gas chromatography device and the process of identifying and measuring the substances will be carried out,” he explained.
In a relevant development in February, the deputy head of Iran’s Blood Transfusion Organization for technological affairs announced that nucleic acid testing (NAT) screening test is being performed in the country to detect viral diseases like hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and AIDS in blood donation samples.
“One of the new technologies of the Blood Transfusion Organization is the NAT screening test, which is a molecular test for detecting viral diseases like hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and AIDS. Early detection of viral diseases and contamination in the blood increases blood safety and shortens the time it takes for the virus to enter the laboratory,” Abdollah Salek Moqaddam told ANA.
He added that at present, the NAT test is being conducted only in Tehran, and it will be performed in other parts of the country in two months.
Salek Moqaddam also said that antibody screening in donated blood is being performed in developed countries of the world, adding, “Fortunately, devices related to this technology have been provided to all provinces of the country, and this screening test will be operational in the next few days.”
NAT is a molecular technique for screening blood donations to reduce the risk of transfusion transmitted infections (TTIs) in the recipients, thus providing an additional layer of blood safety.
4155/v





















