Iran-Made System Paves Way for DNA, RNA Analysis in Biology Labs
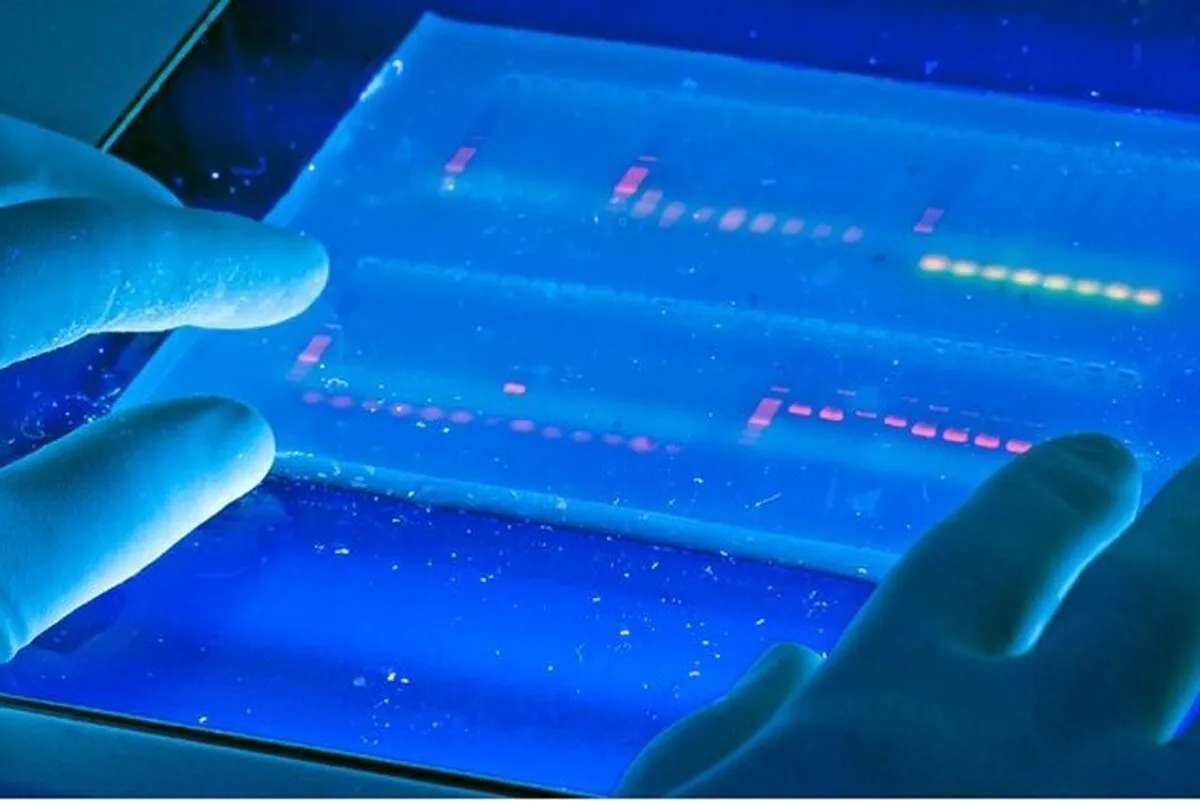
“One of our products is the GelDoc device, which has been upgraded compared to older models. GelDoc is an advanced laboratory device used for imaging and documenting electrophoresis gels. In biology and microbial laboratories, to examine molecules such as DNA, RNA or proteins, samples are placed on an electrophoresis gel and the molecules are separated in the gel by passing an electric current. After this separation, we need an imaging system to view and record the results, and GelDoc systems are used in this field,” said Romisa Sae’edi, a technologist at the knowledge-based company.
“This device allows for gel electrophoresis imaging with an integrated system and has a built-in mini PC. It is also programmed in such a way that all camera parameters, including contrast and sharpness, can be changed,” she added.
“The GelDoc has a touch screen monitor and users can view, rotate and zoom images with it. This complete package makes working with laboratory gels much easier and more accurate than before,” Sae’edi noted.
A GelDoc, also known as a gel documentation system, gel image system or gel imager, refers to equipment widely used in molecular biology laboratories for the imaging and documentation of nucleic acid and protein suspended within polyacrylamide or agarose gels.
Genetic information is stored in DNA. Polyacrylamide or agarose gel electrophoresis procedures are carried out to examine nucleic acids or proteins in order to analyze the genetic data. For protein analysis, two-dimensional gel electrophoresis is employed (2-DGE) which is one of the methods most frequently used in comparative proteomic investigations that can distinguish thousands of proteins in a single run.
Proteins are separated using 2-DGE first, based on their isoelectric points (pIs) in one dimension and then based on their molecular mass in the other. After that, a thorough qualitative and quantitative analysis of the proteomes is performed using gel documentation with software image assessment methods on the 2-DGE gels stained for protein visibility. Gels are typically stained with Ethidium bromide or other nucleic acid stains such as GelGreen.
4155/v





















