Iranian Scientists Decode Role of Ghrelin in Regulating Bird Appetite
In a pioneering study conducted under the supervision of Morteza Zendehdel Kheybari, a full professor of physiology at the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Tehran, in collaboration with Kimia Mahdavi, a researcher and PhD student in physiology at this faculty, and Hamed Zareyee, an associate professor of the Department of Biology at the Islamic Azad University’s Central Tehran branch, the complexities of the function of the ghrelin hormone and its interactions with the neural networks involved in regulating bird appetite were examined from a new perspective, and the results of this study indicate the different functions of this hormone in mammals and birds.
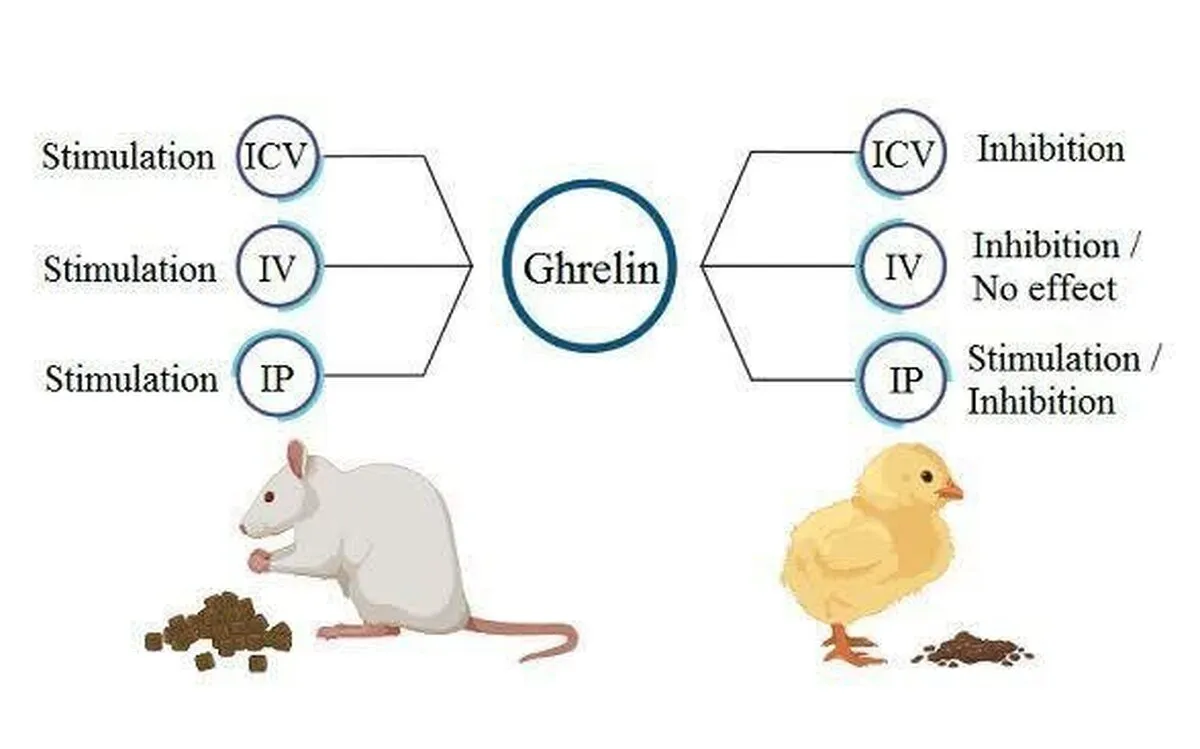
“This article comprehensively examines the biological structure and function of the peptide hormone ghrelin, as one of the key regulators of energy balance and appetite in birds. It also uses the latest scientific findings to show that, unlike mammals, where ghrelin is mainly considered an appetite stimulant, the role of this hormone in birds is more complex and sometimes contradictory in nature and can also exhibit appetite suppressant properties,” Zendehdel Kheybari said.
“One of the distinguishing points of this study from other studies is the comprehensive examination of the complex interactions of ghrelin with multiple neuropeptide networks, like the corticotropin, opioid, dopamine, serotonin, cannabinoid, GABAergic and adrenergic systems, to better understand the role of ghrelin in appetite regulation, which provides a comprehensive and multifaceted picture of this hormone,” he added.
"The present study, beyond advancing the understanding of the neural and hormonal mechanisms of appetite regulation in birds, also opens new horizons for the clinical applications of ghrelin in the field of veterinary medicine," Zendehdel Kheybari underlined.
Ghrelin is a hormone your stomach produces and releases. It signals your brain when your stomach is empty and it’s time to eat. Ghrelin levels increase between mealtimes and decrease when your stomach is full. People who have obesity often have low ghrelin levels, while people who significantly restrict their calorie intake have high ghrelin levels.
Ghrelin and leptin are two of many hormones that control your appetite and fullness. They’re involved in the vast network of pathways that regulate your body weight. Leptin decreases your appetite, while ghrelin increases it.
Ghrelin is made in your stomach and signals your brain when you’re hungry. Your fat cells produce leptin. Leptin lets your brain know when you have enough energy stored and feel “full”.
4155/v





















