Role of Nickel in EV Battery Manufacturing

The advent of electric vehicles (EVs) exemplifies a key step in the green transition, marking a significant leap forward in our journey to combat climate change and reduce fossil fuel dependency, the Innovation News Network reported.
Central to this journey is lithium-ion batteries – the lifeblood that fuels these eco-friendly transportation alternatives. These batteries power our EVs and are crucial components in various modern technologies.
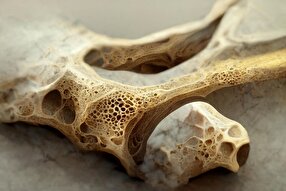
Among the key ingredients of lithium-ion batteries, nickel stands out due to its unique properties. Its energy density and capacity retention make it essential in EV battery manufacturing.
The demand for nickel in EV battery manufacturing is on an upward trajectory, given the surge in EV production worldwide, thereby shedding light on its indispensable role within the industry.
This article explores how nickel usage patterns might evolve in response to emerging trends within the electric vehicle sector.
Undeniably, lithium-ion batteries, with their high energy density and long cycle life, have revolutionised modern technology, playing an indispensable role in the proliferation of electric vehicles and portable electronic devices.
The fundamental features such as battery longevity and charge efficiency propel these advancements. Battery longevity refers to the ability of a battery to maintain its performance over time without significant degradation or need for replacement.
This is crucial in electric vehicles, where the cost and inconvenience associated with frequent battery replacements could undermine user confidence and acceptance. On the other hand, charge efficiency pertains to how much energy a battery can store per unit of electricity consumed during charging.
High charge efficiency reduces energy waste while accelerating charging speed, contributing significantly to making electric vehicles more practical for everyday use. In addition to these benefits, lithium-ion batteries also pose certain challenges that technological advancements and safety measures must address.
Lithium-ion batteries contain hazardous materials that can lead to serious safety incidents if not properly managed — hence the importance of incorporating robust safety measures into their design and usage protocols.
These may include protective circuits that prevent overcharging or thermal runaway, as well as advanced cooling systems that regulate temperature during operation. Furthermore, recycling challenges associated with lithium-ion batteries underscore the need for developing more sustainable practices within this industry sector.
As these batteries reach end-of-life status in increasing numbers due to widespread usage in electric vehicles and other applications, efficient methods for recovering valuable materials like nickel become ever more critical from an environmental conservation and resource management standpoint.
In the realm of battery technology, a direct correlation exists between the concentration of this transition metal and the energy density, with increased amounts leading to heightened performance.
The sourcing and refining processes of nickel play a pivotal role in defining its effectiveness within batteries used for electric vehicles. Nickel, when refined and alloyed suitably, enhances the properties of the battery components by increasing their energy density.
This superior energy density directly translates into improved performance parameters such as extended driving range and longer battery life for electric vehicles.
To address challenges associated with sourcing nickel, extensive recycling initiatives have been established to recover nickel from spent batteries efficiently while minimising environmental harm.
Despite these efforts, the demand for this valuable metal continues to outpace supply due to rapid growth in EV production. Research is being conducted on poten tial substitutes for nickel that could maintain high energy densities without compromising efficiency or affordability.
While finding an effective substitute remains elusive, continuous technological advancements suggest optimism for future breakthroughs in this arena.
The surge for energy-efficient transportation has significantly escalated the requirement for nickel in EV battery manufacturing, presenting both opportunities and challenges in the global market.
One fascinating statistic shows that global nickel demand is projected to increase six-fold by 2030 due largely to the burgeoning electric vehicle market.
The increased demand has led to several growth prospects in nickel mining and refining sectors, further intensifying nickel’s economic influence on a global scale.
However, this situation also presents significant nickel-sourcing challenges due to environmental considerations linked with mining operations and geopolitical issues concerning supply chain security.
Moreover, as the use of nickel-rich batteries increases, so does the importance of addressing battery safety concerns, given their thermal stability.
Despite these potential hurdles, there are promising solutions worth exploring:
Recycling nickel batteries: Developing effective recycling methods can help secure a more sustainable supply of nickel while mitigating environmental impacts;
Nickel substitute potential: Research into alternative materials that could reduce the need for nickel in batteries is ongoing. This research could potentially lessen the industry’s reliance on this metal; and
Improving extraction methods: Technological advancements and improved practices could address some concerns related to sourcing by making extraction processes more efficient and less environmentally damaging.
While the electric vehicle industry’s demand for nickel presents specific challenges, those obstacles may be overcome through innovative solutions like battery recycling, exploration of substitution possibilities and improvements in extraction methodologies.
One pioneering company looking to address these issues is Queensland Pacific Metals (QPM). Through QPM’s industry-leading TECH Project, the company is establishing a sustainable process to produce high-purity nickel to reinforce global supply chains.
Predicting future trajectories in utilising this metallic element, especially within the realm of electric vehicles, necessitates an understanding of market dynamics and technological advancements while acknowledging the potential environmental implications.
The dependence on nickel in EV battery manufacturing underscores its importance in achieving a carbon-neutral future. However, as demand escalates, so does pressure on nickel’s market dynamics, including pricing and supply chain stability.
Further attention is drawn to geopolitical implications resulting from the uneven global distribution of nickel resources, which could potentially exacerbate trade tensions or conflicts.
In summary, it is evident that nickel plays a pivotal role in the electric vehicle industry. The high energy density offered by lithium-ion batteries with significant nickel content boosts their demand and usage, thus steering growth in this sector.
Given its indispensable contribution to battery technology and consequently, to sustainable transportation, the future trends point towards an escalating reliance on nickel.
Therefore, further research into environmentally friendly methods of mining and recycling this valuable resource becomes imperative.
4155/v