Iranian Researchers Achieve Technology to Desalinate Salty Wastewater by 72%
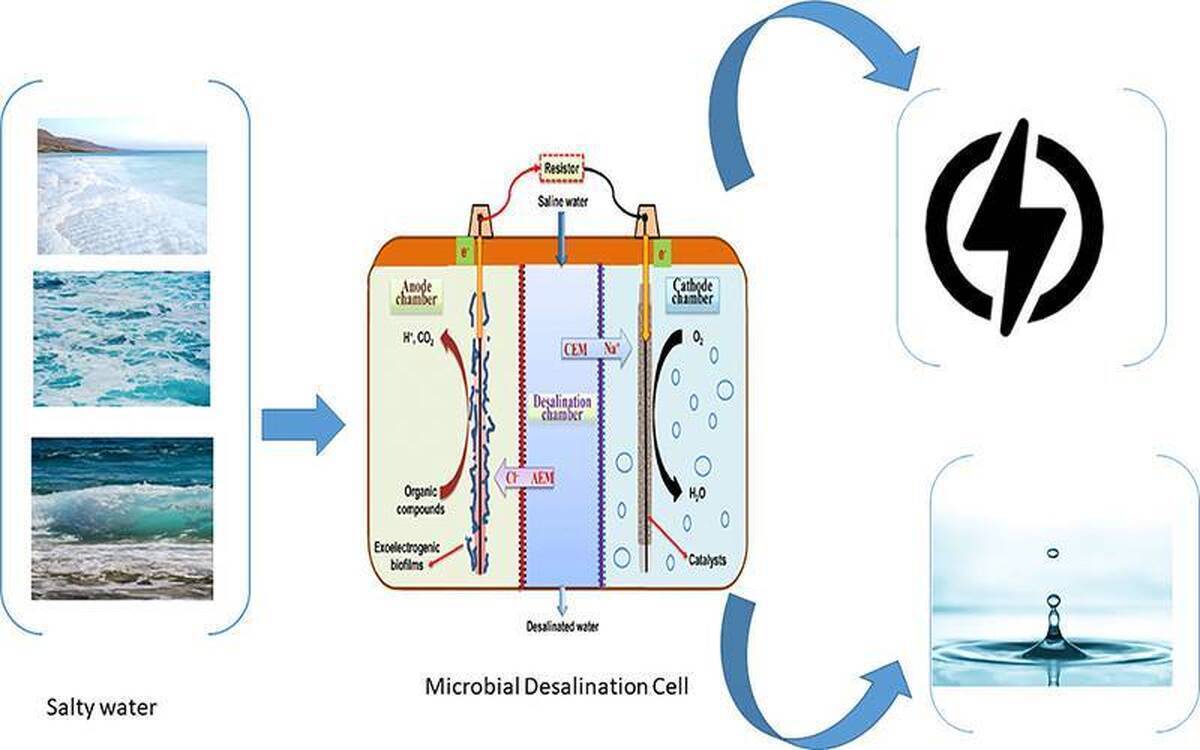
A team of researchers in the field of environment department at NRI succeeded in desalinizing the salty effluent of a power plant by 72% using the microbial desalination cell (MDC).
A microbial desalination cell (MDC) is a biological electrochemical system that implements the use of electro-active bacteria to power desalination of water in situ, resourcing the natural anode and cathode gradient of the electro-active bacteria and thus creating an internal supercapacitor. It is a new and modern technology that can minimize energy consumption and increase fresh water production.
Morteza Jalali Lichaei, the Director of the NRI environmental research department and the xecutive director of the project, noted that water is one of the main needs of combined-cycle and heating power plants.
He explained that one of the effluents produced in these power plants and gas-fouled plants equipped with turbine inlet air cooling system is saline effluent, which is a wastewater stream containing a combination of dissolved salts, hardness ions, organic content, nutrients, or other metals. The effluent is mixed with other wastewaters or discharged in evaporation ponds after pH adjustment, the researcher added.
Saying that due to the distinct composition and saturation indices (SI) of these wastewaters, their treatment and desalination with the help of Reverse Osmosis Membrane (RO) is not possible or economical, he added, “The discharge of these effluents into surface waters also has adverse effects and causes the deterioration of the soil and the reduction of the ability of water to penetrate into the ground, and also the salts existing in these effluents accumulate with (mixed with) the mineral salts of agricultural soil and gradually cause wilting or slow growth of plants. Therefore, desalination of these wastewaters is very important.”
“In this technology, energy production, desalination and reduction of organic load are carried out simultaneously, and for that, it has a great potential for treating of various types of contaminated water, particularly for use in small rural communities and remote areas,” Jalali Lichaei added.
“In this project, the possibility of using microbial desalination cell (MDC) system for the desalination of the salty wastewater of a power plant was studied for the first time. The findings showed that despite the existence of numerous salt compositions in the salty effluent of the power plant, the MDC system with biological cathode (algae), continuous exposure, and the optimal concentration of the carbon source in the anode compartment has an acceptable potential for desalination of the salty effluent of the power plant,” the researcher added.
The executive director of the biological desalination project added that the best results were obtained at a conductivity of 55 millisiemens/cm, which is the highest level of salinity of salty power plant effluents, and the studied system showed acceptable performance in all three idexes of microbial desalination cells (desalination rate, electric power generation, and removal of organic load.”
Jalali Lichaei went on to note that they had used air-cathode MDC instead of biological cathode as the air-cathode showed a considerable superiority in terms of electric power generation. Also, in the desalination rate and removal of organic load, better results were obtained.”
“The output of the microbial desalination system can be used for special purposes, such as irrigation of plants resistant to salinity, agriculture in sandy soils with proper drainage, non-drinking uses such as washing different places, concrete production, etc. Also, these systems can be used in combination with reverse osmosis (RO) treatment units and for pre-purification of the input of these units and cause a reduction in the amount of energy consumed in these units,” the NRI researcher concluded.
4155/i





















